Building a Business Model Canvas for Your Startup
A business model canvas (BMC) is a template that summarizes
the nine key components of a business model in a single diagram.
Since a BMC is used primarily to organize business model
hypotheses, you should expect it to change over time so you can keep track of
the different iterations of your BMC to observe how your business model
evolves.
Each component of the BMC is organized within larger
groupings: customers, finances, or infrastructure.
 |
| Business Model Canvas |
You may have noticed that the value propositions
section is not included within the categories in the image above.
This is your starting point. It describes your vision for
how your offering will be successful, its features and benefits, and ideas for
an initial minimum viable product (MVP).
Let’s consider our car wash delivery service. The service
vision is that it will eliminate the need for
The features and benefits are online order, while the
minimum viable product is that customers will be able to register online and make
order regardless of the aesthetic of the website or application.
The goal of the Value Proposition section is to
present a compelling narrative to achieve buy-in from both early adopters and
investors.
The value proposition brief should outline how the offering
will solve a problem or fulfill a need—in short, its value to the customer.
An example of value proposition is: “Customers wastes $
on trainers and behavior modification. Es provides mutual understanding between
dog and owner. Two-way translation devise attaches to any collar and waterproof.”
After the Value Proposition, the next section that you
should fill out relates toyour customers. It consists of three components:
·
Customers segments, or the target customers for
your service or product
·
Channels, or how you will deliver your service
to your customers
·
Customer relationships, or how you will acquire,
retain, and attract new customers.
Let’s categorize the following elements as customer
segments, customer relationships, or channels.
|
Elements |
Category |
comments |
|
You envision a loyalty program, in which current customers
receive money back when they refer new customers to your company |
Customer relationships |
This is way to retain customers once they have made purchase |
|
You want to sell your product through vetenarian offices in
order to make your product seem more scientifically legitimate. |
channels |
This is where customers will be able to purchase your product. |
|
You make a list of Instagram influencers who also own dogs to
see if they would post about your product |
Customer relationships |
customer relationships are about attracting and retaining
customers. you can get earned media from influencers to attract their
followers. |
|
you target busy corporate workers in Lagos state. |
customer segments |
they are your target market |
|
you set up an extensive outreach program, including welcome
emails, how-to guides, and periodic phone calls checking in with customers. |
Customer relationships |
This is all about customer retention. |
Next, you should evaluate the infrastructure you need to
develop or secure in order to be successful. This includes:
·
Key resources, or critical physical, financial,
human, and intangible assets;
·
Key activities, or processes necessary to
deliver value to your customers; and
·
Key partners, or relationships that provide key
resources that you cannot produce yourself.
Customer education is an example of key activities
especially when creating a new market with a never-before-seen product. Examples
of key activities also include marketing and device maintenance. These are the
ongoing activities that will support your business.
Key resources include your engineering genius, seed money
and patent for translation device.
Key partners include: Device manufacturer, Instagram
influencer and veterinarians
Finally, you need to assess your cost structure and revenue
streams to determine that your business model makes financial sense.
To do this, you will need to answer four questions.
How will you generate revenue? Will it be a one-time purchase?
Will you use a subscription or freemium model? Will you try to earn additional
revenue through referrals or affiliate links?
How many products will you sell? This estimate is based on
the market size hypothesis you calculated in the previous
lesson, combined with channel volume potential estimates.
How much will you charge? You will need to take into account
your costs, as well as the pricing strategy you want to carry out (penetration
pricing, competitive pricing etc.).
Will this be a profitable business? You don’t need exact
numbers, but it is important to have enough of an estimate to decide whether to
move on to the next stage of the customer development process.
Sometimes, startups need to modify the business model canvas
to account for limited information about new markets.
One popular modified version is the lean canvas,
which includes less about logistics and more about the customer—specifically,
assumptions made about the customer’s problems, and how the business will
verify those assumptions. (another modified version is the opportunity canvas,
which is used for pivoting existing offerings rather than developing a new product.).
 |
| Lean Canvas |
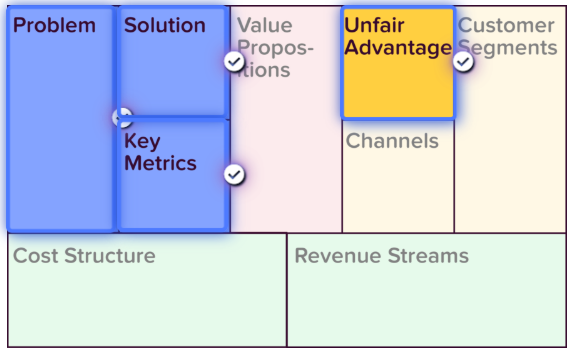
The lean canvas (read
more) looks very much like the business model canvas, with the exception of
four changes.
“Problem” replaces “Key Partners.” This section answers the
question “what is the problem you are trying to address and ow do you
understand it?”
“Key Activities” becomes “Solution.” This section presents
the best possible solution to the problem you are investigating.
“Key Metrics” replaces “Key Resources.” Here you will
include the actions and metrics that matter the most when proving your business
hypotheses.
“Customer Relationships” becomes “unfair Advantage.” These
are traits that will give your company a competitive edge and can’t easily be
bought or copied. Many startups will have to leave this box blank at first!
In general terms, the lean canvas takes the focus away from operations
and places the emphasis on ideas.
Why do you think this makes the lean canvas better suited to
new businesses?
It facilitates experimentation and discovery to help achieve
goals. The addition of key metrics encourages entrepreneurs to measure their success
and adapt accordingly.
It emphasizes new ideas over traditional strategies. The focus
of the lean canvas is customer problems and your unique, hard-to-copy solution.
Execution is secondary, and open to revision.
In conclusion, some of the questions components of a typical
BMC answer are
Key activities: What are the processes requires to
deliver value to customers?
Channels answered the question of How the product
will get to your customers and how much it will cost to get the product into
customers’ hands.
Cost structure: How much does it cost to operate your
business?
Customer relationships: How will you attract customers?
How will you retain them once you’ve made a sale? How will you grow additional
revenue from them over time?
Key resources: What are the physical, financial,
human, and intangible assets that are critical to the company’s success? Where
will you find them and how will you acquire them?
Revenue Streams: How will you generate income from customers?
How much will you charge?
Key partners: Who can you team up with to procure the
capabilities or resources that you require, but can’t develop yourself?
Customer segments: Who are you selling to? What are
the characteristics of your typical customer?
Click here
to download a business model canvas template to create your own BMC
 |
| Business Model Canvas Template |