Startup Essentials: What You Need To Know When Creating Your Startup
 |
| Nigerian Startup Team |
To be successful, startups shouldn’t just try to be a scaled-down version of a large company.
For existing companies with a known market, traditional
product development can work just fine. But if you’re unsure about what you’re
selling and who you’re going to sell it to, startup model might be more
appropriate.
But what
exactly is a startup?
Startup, as defined by Steve Blank, is a temporary organization
in search of a scalable, repeatable, profitable business model.
Essentially, this means: Startups are adaptable organizations whose primary
goals is to find a business model—not execute one. When they find a successful business
model and scale up to execute it, they turn from a startup into a regular
company.
Example of a startup are: A student wants to start a social
network for children or an engineer designing an app to sell.
Startup Customer
Development Method
All startups face the risk of not finding customers for
their product or service. To mitigate this, Blank introduced the customer
development method, a process to help startups systematically search for a
successful business model.
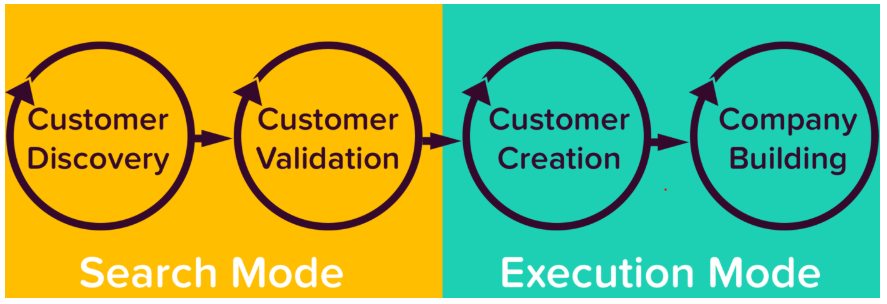 |
| Startup Customer Development Method |
This method is divided into four stages: the first two test
the business model (search mode), and the second two execute and scale
the business (execution mode).
1.
Customer discovery: This translate founders’ vision
into business model hypotheses and test them. In testing these hypotheses, you
will discover information about your customers and determine product-market
fit.
2.
Customer validation: Testing resulting business
model for repeatability and scalability.
3.
Customer creation: establish market, position,
and build demand.
4. Company building: Grow organization to support execution of business model
In its early days, a startup operates in “search model”—its business model is just a collection of unproven hypotheses.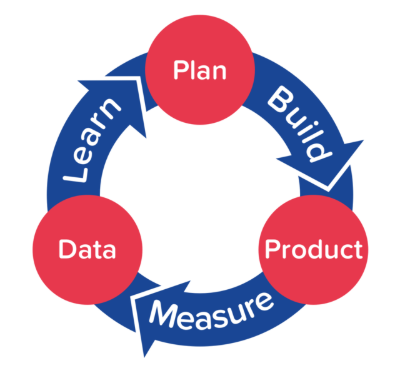 |
| Build-Measure-Learn Loop |
If a hypothesis fails, it doesn’t mean the business is
doomed. A startup can always pivot, or radically change its focus. For example,
Twitter was originally a podcast-subscription network called Odeo.
When iTunes entered the market, Odeo couldn’t compete—instead, they focused on
building a microblogging platform, and history was made! Once Odeo’s failure was inevitable, the
company would hold “hackathons” for employees to develop their own ideas—Twitter
was the brainchild of Odeo engineer Jack Dorsey.
When choosing your startup team, it’s important to select
for traits that will maximize the company’s chances for success—without Jack
Dorsey’s creative problem-solving skills, Twitter would never have been born.
Startup
Team Build: Traits and Skills to Lookout for
Some of the key traits and skills that would benefit a
fledging startup are:
1.
Curiosity: curiosity helps in the search
for a repeatable, scalable business model.
2.
Passion: passion can help you keep going when
you’re still in the middle of a difficult process.
3.
Comfort with failure: failure can be
useful learning experience, and it’s important to have people on board who view
it that way.
4.
Quick, reversible decision-making: in the
early days, it’s important not to make too many irreversible decisions, in case
you have to pivot!
The traits listed above are not in particular order.
But when
is a startup no longer considered a startup?
Once a startup has found its scalable, repeatable business
model, and it has proven customer demand, it can shift its efforts toward execution
mode.
At this point, the startup officially becomes a company
focused on administration and growth.
Conclusion
- Little revision on What we’ve learnt so far about startup.
- A startup model differs from traditional product development in that for a startup the product and market are unknown.
- Turning the founders’ vision for the company into business model hypothesis and testing them is the main goal during customer discovery.
- Spending should be limited as much as possible until execution mode.
- The Building-Measure-Learn loop uses iterative design to develop a minimum viable product (MVP).
- If one of your business model hypotheses fail, you could pivot.